
React学习
React学习
在学习React时为了更好处理数组以及对象需要更仔细了解数组以及对象的一些方法。这里做一点简单介绍。
原型
例如,我们有一个 user 对象及其属性和方法,并希望将 admin 和 guest 作为基于 user 稍加修改的变体。我们想重用 user 中的内容,而不是复制/重新实现它的方法,而只是在其之上构建一个新的对象。 (跟类继承有什么差别?)

数组、对象解构
Rest 参数与 Spread 语法 (javascript.info)
在JavaScript中,函数支持任意数量的参数.这在其他语言是并不多的,主要使用Rest参数以及Spread语法.
React 课程
Side effect

Render logic must produce no side effects

Batched State Update


Lazy render
使用函数作为useState参数,只在初始渲染时调用.
const [fun, setfun] = useState(()=>{console.log('我是初始化函数')});如果传入函数调用比如func(),那么每次渲染时都会调用这个函数,这是不必要的.
event delegation

Effect

use effect to in sync with external world
events used to react to an event
Loading State

UseEffect Dependency


CleanUp function

KeyPress Event
useEffect(() => {
document.addEventListener("keydown", (e) => {
if (e.code === "Backspace") {
// setSelectedID(null);
handleRestID();
}
return () => {
document.removeEventListener("keydown");
};
});
}, []);Hook


- Hooks can only be called at the top level
- only call hooks from react function

利用本地存储(LocalStorage)或者数据库与State同步.

Ref


Not trigger re-render
Custom Hook

Class-Based React
Before React v16.8 …

Child to component communication
Props
useReducer

function reducer(state, action) {
console.log(state, action); //现在的state,action为dispatch传入的值
return state+action;//返回新的state
}
-------------------------------------
const [count, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, 0); // 0初始值 reducer方法function reducer(state, action) {
console.log(state, action);
switch (action.type) {
case "dec":
return { ...state, count: state.count - state.step };
case "inc":
return { ...state, count: state.count + state.step };
case "setCount":
return { ...state, count: action.payload };
case "setStep":
return { ...state, step: action.payload };
case "reset":
return initialState;
default:
throw new Error("Invalid action type");
}
}




多使用js中数组和对象的一些方法.比如数组的map,reduce等,以及rest,spread语法
React Router
使用Vite而不是已经过时的creat-react-app

vite配置ESLint,安装vite的eslint插件
npm i vite-plugin-eslint --save-dev在vite.config.js中配置eslint
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react";
import eslint from "vite-plugin-eslint";
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [react(), eslint()],
});
项目目录下已经有了.eslintrc.cjs
module.exports = {
root: true,
env: { browser: true, es2020: true },
extends: [
'eslint:recommended',
'react-app',
'plugin:react/recommended',
'plugin:react/jsx-runtime',
'plugin:react-hooks/recommended',
],
ignorePatterns: ['dist', '.eslintrc.cjs'],
parserOptions: { ecmaVersion: 'latest', sourceType: 'module' },
settings: { react: { version: '18.2' } },
plugins: ['react-refresh'],
rules: {
'react-refresh/only-export-components': [
'warn',
{ allowConstantExport: true },
],
},
}

多页应用 (MPA,Multi-Page Application) 是一个由多个 HTML 页面组成的网站,主要在服务器上渲染。当您导航到一个新页面时,您的浏览器会从服务器请求一个新的 HTML 页面。Astro 是一个 MPA 框架。 传统的 MPA 框架还包括 Ruby on Rails、Python Django、PHP Laravel、WordPress、Joomla、Drupal 和静态网站构建器,如 Eleventy 或 Hugo。
单页应用(SPA,Single-Page Application) 是一个由单个 JavaScript 应用程序组成的网站,该应用程序在用户浏览器中加载,然后在本地呈现 HTML。SPA 也可能在服务器上生成 HTML,但 SPA 的独特之处在于它们能够在浏览器中将您的网站作为 JavaScript 应用程序运行,以便在您导航时呈现新的 HTML 页面。此外, Next.js、Nuxt、SvelteKit、Remix、Gatsby 和 Create React App 都是 SPA 框架的示例。
Astro 是一个 MPA 框架。然而,Astro 也不同于其他 MPA 框架。它的主要区别在于它使用 JavaScript 作为其服务器语言和运行时。传统的 MPA 框架会让您在服务器上编写不同的语言(Ruby、PHP 等)并在浏览器上编写 JavaScript。在 Astro 中,您总是只是在编写 JavaScript、HTML 和 CSS。这样,您可以在服务器和客户端上呈现您的 UI 组件(如 React 和 Svelte)。
其结果是开发人员体验很像 Next.js 和其他现代 Web 框架,但具有更传统的 MPA 站点架构的性能特征。

使用Link或者NavLink链接进行跳转


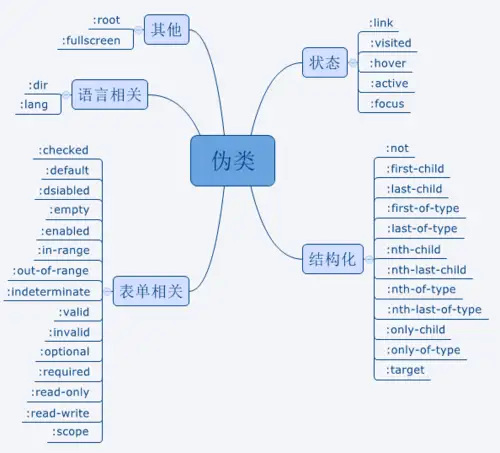
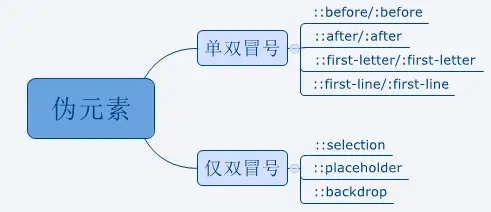
styling

这里主要介绍CSS Module方法.
创建components,比如AppLayout.jsx,再创建css,比如AppLayout.module.css
.nav {
background-color: orangered;
}
.nav ul {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
list-style: none;
background-color: orangered;
}
import styles from "./pageNav.module.css";
export default function PageNav() {
return (
<nav className={styles.nav}>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink to="/pricing">pricing</NavLink>
</li>
<li>
<NavLink to="/product">product</NavLink>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
);
}
注意:global()的使用
全局css直接在App.jsx中使用即可.
Nested Routes and index Route
嵌套路由
<Route path="app" element={<AppLayout />}>
<Route path="cities" element={<p>List of cities</p>} />
<Route path="countries" element={<p>Countries</p>} />
<Route path="form" element={<p>Form</p>} />
</Route>import styles from "./Sidebar.module.css";
import AppNav from "./AppNav";
import Logo from "./Logo";
import { Outlet } from "react-router-dom";
export default function Sidebar() {
return (
<div className={styles.sidebar}>
<Logo />
<AppNav />
<Outlet /> //出口
<footer className={styles.footer}>
<p className="styles copyright">
© copyright {new Date().getFullYear()} by WorldWise Inc.
</p>
</footer>
</div>
);
}
The Url for state managemet

dynamic routes with url paremeter
使用Routepath属性对值匹配
<BrowserRouter>
<Routes>
{/* <Route path="/" element={<HomePage />} /> */}
<Route index element={<HomePage />} />
<Route path="product" element={<Product />} />
<Route path="pricing" element={<Pricing />} />
<Route path="app" element={<AppLayout />}>
<Route
index
element={<CityList cities={cities} isLoading={isLoading} />}
/>
<Route path="cities/:id" element={<City />} />
<Route
path="cities"
element={<CityList cities={cities} isLoading={isLoading} />}
/>
<Route
path="countries"
element={<CountriesList cities={cities} isLoading={isLoading} />}
/>
<Route path="form" element={<p>Form</p>} />
</Route>
<Route path="login" element={<Login />} />
<Route path="*" element={<PageNotFound />} />
</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>可以使用Link进行路由跳转,使用to指定
<Link className={styles.cityItem} to={`${id}?lat=${position.lat}&lng=${position.lng}`}>
<span className={styles.emoji}>{emoji}</span>
<h3 className={styles.name}>{cityName}</h3>
<time className={styles.data}>({formatDate(date)})</time>
<button className={styles.deleteBtn}>× </button>
</Link>使用useParams以及useSearchParams获取url的参数.
const x = useParams()
console.log(x)
const params = useSearchParams();
console.log(params);假设url最后是73930385?lat=38.727881642324164&lng=-9.140900099907554
那么73930385就是x,parms就是一个对象,包含lat以及lng.
useNavigate
编程式导航,而不是使用<Link>或者<NavLink>
首先也需要声明路由
const navigate = useNavigate();
<Button
type="back"
onClick={(e) => {
e.preventDefault(); //如果在表单form里使用,点击按钮会刷新 所有需要避免默认行为
navigate(-1);
}}
>
← Back
</Button><div
className={styles.mapContainer}
onClick={() => {
navigate("form");
}}
>
<h1>Map</h1>
<h1>
Position:{lat},{lng}
</h1>
{/* <button onClick={() => setSearchParams({ lat: 23 })}>Click me</button> */}
</div>Navigate组件
也是react-router-dom库里的东西,之前还使用过了BrowserRouter, Route, Routes这些组件以及useNavigate,useSearchParams以及useParams这些hooks.
<Route path="app" element={<AppLayout />}>
<Route
index
element={<Navigate to="cities"/>}
/>
<Route
path="cities"
element={<CityList cities={cities} isLoading={isLoading} />}
/>
<Route path="cities/:id" element={<City />} />
<Route
path="countries"
element={<CountriesList cities={cities} isLoading={isLoading} />}
/>
<Route path="form" element={<Form />} />
</Route>使用Navigate重定向到先定义的Route,但是存在浏览器上无法使用浏览器后退.
使用replace替换.
浅析react-router@6版本中,Navigate组件重定向路由的使用 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
import React from "react";
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link } from "react-router-dom";
import { Routes, Route, Navigate, useRoutes } from "react-router";
const Child = () => {
return <div>1 aaa</div>;
};
const Child2 = () => {
return <div>2 bbb</div>;
};
export default function App() {
return (
<div>
<Router>
<Link to={"/aaa"}>to 1 aaa</Link>
<hr />
<Link to="/bbb">to 2 bbb</Link>
<hr />
<Link to="/ccc">to 3 cc</Link>
<hr />
<Routes>
<Route path="aaa" element={<Child />}></Route>
<Route path="bbb" element={<Child2 />}></Route>
<Route path="*" element={<Navigate to={"aaa"} replace />}></Route>
</Routes>
</Router>
</div>
);
}这段代码,只能访问
/aaa和/bbb,访问其他路由都会被捕获并重新跳转至/aaa,Navigate的replace如果不加的话则无法后退,因为/aaa—>/sdjfklsadj—>/aaa的场景下,错误的路由实际上会被记录到历史栈中,点击后退会退回到错误的路由,并又再次匹配到且跳转会/aaa,加了replace后历史栈则会变成/aaa->/aaa
Context
解决props drilling问题,简单情况下的解决方案是安排好组件的结构。


具体使用方法,使用createContext,provider以及useContext.
// 1) create a new CONTEXT
const PostContext = createContext();
// 2) provide value to child components
<PostContext.Provider
value={{
posts: searchedPosts,
onAddPost: handleAddPost,
onClearPosts: handleClearPosts,
searchQuery,
setSearchQuery,
}}
>
<section>
<button
onClick={() => setIsFakeDark((isFakeDark) => !isFakeDark)}
className="btn-fake-dark-mode"
>
{isFakeDark ? "☀️" : "🌙"}
</button>
<Header />
<Main posts={searchedPosts} onAddPost={handleAddPost} />
<Archive onAddPost={handleAddPost} />
<Footer />
</section>
</PostContext.Provider>
//3. consuming context
const { onClearPosts } = useContext(PostContext);
return (
<header>
<h1>
<span>⚛️</span>The Atomic Blog
</h1>
<div>
<Results />
<SearchPosts />
<button onClick={onClearPosts}>Clear posts</button>
</div>
</header>
);
Provier组件下的组件能使用useContext获取提供的value.
创建自己的Context
import { createContext, useState } from "react";
import { faker } from "@faker-js/faker";
function createRandomPost() {
return {
title: `${faker.hacker.adjective()} ${faker.hacker.noun()}`,
body: faker.hacker.phrase(),
};
}
const PostContext = createContext();
function PostProvider({ children }) {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState(() =>
Array.from({ length: 30 }, () => createRandomPost())
);
const [searchQuery, setSearchQuery] = useState("");
// Derived state. These are the posts that will actually be displayed
const searchedPosts =
searchQuery.length > 0
? posts.filter((post) =>
`${post.title} ${post.body}`
.toLowerCase()
.includes(searchQuery.toLowerCase())
)
: posts;
function handleAddPost(post) {
setPosts((posts) => [post, ...posts]);
}
function handleClearPosts() {
setPosts([]);
}
return (
<PostContext.Provider
value={{
posts: searchedPosts,
onAddPost: handleAddPost,
onClearPosts: handleClearPosts,
searchQuery,
setSearchQuery,
}}
>
{children}
</PostContext.Provider>
);
}
export { PostContext, PostProvider };使用PostContext以及PostProvider
<PostProvider>
<Header />
<Main />
<Archive />
<Footer />
</PostProvider>此外还可以将Context与Hooks结合,
State Management





Performance optimization tools
-
防止多次渲染
-
提升应用响应速度以及自适应
-
减小Bundle大小


使用React开发者工具 Profiler调优 将组件以children或者props形式传入
import { useState } from "react";
function SlowComponent() {
// If this is too slow on your maching, reduce the `length`
const words = Array.from({ length: 100_000 }, () => "WORD");
return (
<ul>
{words.map((word, i) => (
<li key={i}>
{i}: {word}
</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}
export default function Test() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<h1>Slow counter?!?</h1>
<button onClick={() => setCount((c) => c + 1)}>Increase: {count}</button>
<SlowComponent />
</div>
);
}
// 比较前后差异
function Counter({children}){
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<h1>Slow counter?!?</h1>
<button onClick={() => setCount((c) => c + 1)}>Increase: {count}</button>
{children}
</div>
);
}
export default function Test() {
return (
<div>
<Counter><SlowComponent/></Counter>
</div>
);
}Memo



默认情况下,父组件render,所有子组件都会重新render.
memo 用在经常render的组件,其props通常不变,而且通常加载较慢.


props传给子组件时,如果传的是函数和对象,在re-render之后内存地址改变,所以变得不同后,Memo就变得不work了.
解决方案:useCallback useMemo
useMemo


const archiveOptions = useMemo(() => {
return {
show: false,
title: `Post archive in addition to main posts ${posts.length}`,
};
}, [posts.length]);
<Archive archiveOptions={archiveOptions} onAddPost={handleAddPost} />使用useMemo,使得在已经使用了Memo缓存子组件之后,传递对象props,只要useMemo的依赖不改变,则archiveOptions就不会改变,使得传递对象props也能缓存子组件.
useCallback
const handleAddPost = useCallback(function handleAddPost(post) {
setPosts((posts) => [post, ...posts]);
}, []);
<Archive archiveOptions={archiveOptions} onAddPost={handleAddPost} />这样当父组件re-render时,handleAddPost不会变,也就不会在更新子组件.
state的setter函数作为子组件的props,父组件render,子组件不会重新render
memo目的是缓存子组件,使得在传递相同props下,父组件render,其不再render
而由于父组件render时,对象与函数会再次创建,因为非Primitive数据,值不再相同,所以需要使对象与函数稳定
而useMemo与useCallback就是分别使得对象与函数稳定的,此外也可以用在useEffect等的依赖上,以及用于存储数据避免每次re-render时的消耗,如果值不变可以使用Lazy state,即使用useState(func);使用func返回值作为state,且只初始化第一次render.
Optimizing Bundle Size with Code spliting
涉及到SPA

Page/Route Level
首先npm run build之后,

得到的bundle,就是只有html,css,js. 到时候就是把这些文件放服务器,然后浏览器下载这几个文件并进行渲染.
可以注意到提示说一些chunks大雨了500kB,这里指的就是我们的js文件.所以需要使用动态导入,或者叫懒加载.
Suspense
const HomePage = lazy(() => import("./pages/Homepage"));
const Product = lazy(() => import("./pages/Product"));
const Pricing = lazy(() => import("./pages/Pricing"));
const Login = lazy(() => import("./pages/Login"));
const AppLayout = lazy(() => import("./pages/AppLayout"));
const PageNotFound = lazy(() => import("./pages/PageNotFound"));
<Suspense fallback={<Spinner />}>
<Routes>
{/* <Route path="/" element={<HomePage />} /> */}
<Route index element={<HomePage />} />
<Route path="product" element={<Product />} />
<Route path="pricing" element={<Pricing />} />
<Route
path="app"
element={
<ProtectedRoute>
<AppLayout />
</ProtectedRoute>
}
>
<Route index element={<Navigate to="cities" replace />} />
<Route path="cities" element={<CityList />} />
<Route path="cities/:id" element={<City />} />
<Route path="countries" element={<CountriesList />} />
<Route path="form" element={<Form />} />
</Route>
<Route path="login" element={<Login />} />
<Route path="*" element={<PageNotFound />} />
</Routes>
</Suspense>
lazy import+Suspense 懒加载配合 Suspense
每个懒加载的组件可以成为chunk,这样做用户如果没有使用到某个组件,服务器也不会发送那个组件,所以浏览器请求的数据就会少一些,初次渲染的东西就要少一些
再次build一下,发现js与css都自动分为了多个chunk,注意chunks与lazy import导入的每个组件并不是一一对应的.




reactive value :state,props以及Derived state/function/props
Attention:in real-world app,a library like react-query should be used to featch data on component mount

useEffect(() => {
setDuration((number * sets * speed) / 60 + (sets - 1) * durationBreak);
}, [number, sets, speed, durationBreak]);在useEffect中更新状态,这很可能导致两次渲染.

Render props pattern
主要是父组件传递给子组件不同的参数render用于渲染子组件的内容
Compound components pattern
<Counter>
<Counter.Label>this is a counter</Counter.Label>
<Counter.Count />
<Counter.Increase icon="+" />
<Counter.Decrease icon="-" />
</Counter>import { useState, createContext, useContext } from "react";
// 1. create Context
const CounterContext = createContext();
// 2.create parent componente
export default function Counter({ children }) {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increase = () => setCount((c) => c + 1);
const decrease = () => setCount((c) => c - 1);
return (
<CounterContext.Provider value={{ count, increase, decrease }}>
<span>{children}</span>
</CounterContext.Provider>
);
}
// 3. create childr element to help implementing the common
function Count() {
const { count } = useContext(CounterContext);
return <span>{count}</span>;
}
function Label({ children }) {
return <span>{children}</span>;
}
function Increase({ icon }) {
const { increase } = useContext(CounterContext);
return <button onClick={increase}>{icon}</button>;
}
function Decrease({ icon }) {
const { decrease } = useContext(CounterContext);
return <button onClick={decrease}>{icon}</button>;
}
// 4. Add child components as properties to parent components
Counter.Count = Count;
Counter.Label = Label;
Counter.Increase = Increase;
Counter.Decrease = Decrease;
React Portal
本质上允许呈现父组件DOM结构之外的元素,同时仍将元素保持在组件树的原始位置.
方便使用模态窗口,工具提示,菜单.
好用的库
1.OMDB IMDB
电影API
2.LeafLet 地图
3.BigDataCloud API - Precise fast and affordable Next Gen API